
What is a Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a virtual currency; it exists online instead of coins or pieces of paper that we carry in our wallets. It will enable you to send money to anyone in the world within seconds without the need for a bank or any other intermediary. The special technology that makes Bitcoin safe is known as blockchain, which safely documents all the transactions made. To put it simply, Bitcoin is a type of money that is entirely online and operates without the use of traditional financial institutions.
Bitcoin is a digital currency that exists only online.
- It is not like coins or paper money that we keep in our wallets.
- You can transfer Bitcoin to any part of the world in real time.
- It does not require a bank or a middleman to make transactions.
- It is safe since it is a technology known as blockchain.
- Overall, Bitcoin is a 100 per cent Internet-based currency that is not dependent on conventional banks.
How Did Bitcoin Start?
Bitcoin was introduced in 2009 by an unknown individual or possibly a team of people, known as Satoshi Nakamoto. This followed immediately after the financial crisis of 2008, when no one could trust their banks anymore.
Bitcoin was invented as an alternative form of money that is not regulated by any government or banks. It is open, as anyone can check all the transactions on the blockchain. It is cash on the internet that operates like cash, which you can pay any person without seeking authorisation.
It is also quick, inexpensive, accessible to everyone with a connection to the internet and is cryptographically controlled, ensuring its safety and nearly impossible to counterfeit. Bitcoin was not digital money only; it was a new approach to thinking about freedom, trust, and control in finance.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin is Digital Money: It’s an online currency that lets you send money globally without banks.
- Blockchain is the Secure Record: Think of it as a shared, unchangeable digital notebook that records all Bitcoin transactions.
- Miners Secure the System: These are like accountants and security guards who solve complex puzzles to verify transactions and add them to the blockchain, earning new Bitcoin as a reward.
- Hashes are Digital Seals: They are unique codes that ensure the information in each block hasn’t been tampered with.
- Wallets Store Your Keys: Your Bitcoin wallet doesn’t hold the Bitcoins themselves, but rather the special “keys” (public and private) you need to access and manage them on the blockchain.
- Bitcoin is Limited Like Gold: Only 21 million Bitcoins will ever exist, making it valuable and scarce.
- Mining is Harder Now: It requires powerful, energy-hungry machines (ASICs) and is mostly done by large mining farms, not individual home users.
What is Blockchain?
Imagine you and your friends are playing a game, and all of you record the points in a notebook. It is written down whenever somebody earns points. So to even things out, everyone has the same notebook. People can not cheat and alter their scores because other people have the actual documentation.
That is the way blockchain works.
- Imagine blockchain as a giant notebook that is shared by all the people in the world.
- Whenever a person sends or receives Bitcoin, they write it down in this notebook.
- As soon as it is written, it is impossible to erase or alter it.
There are numerous replicas of this notebook on computers all over the world, and therefore nobody can cheat.
How Do People Get Bitcoin?
There are two main ways:
- Mining Bitcoin – By working on puzzles and enabling the blockchain to be secure.
Incidentally, mining can be presumed to be the factory in which new Bitcoins are produced.
What Exactly Do Miners Do?
Imagine a large communal board on which people stick the notes. One can find hundreds of individuals in the queue to place their notes. However, before a new page of notes can be pinned, there is someone must unlock a special lock by means of a hard code. The fast machines are used by many folks (miners) simultaneously. Anyone who unlocks the lock first has the privilege of pinning the page and gets a prize to do so.
Transactions waiting
There are a lot of people transferring Bitcoin simultaneously. These outstanding payments are placed in a queue (referred to as the mempool).
Transaction collection is done by miners
The miners will select valid pending payments and bundle them in a block.
Hard puzzle to solve (Proof of Work)
To add that block, miners have to find a special solution to a math puzzle. It does not find (too much guesswork), it watches. Powerful computers are the only ones capable of trying fast enough.
First to solve wins
The miner who has the correct answer is the first and has the right to append his block to the blockchain (the permanent record).
Reward
The victorious miner receives newly minted Bitcoin (block reward) along with the transaction fee costs of the payments included in that block.
Why does this make Bitcoin straight
Cheating is not cheap: To forge history, a cheater would require more computing capability than the honest network to recalculate all that puzzle work—and that is simply impossible.
Everyone can check: As soon as a block has been added, anyone can immediately check it; when it is valid, the network admits it.
locked-in history: The blocks are chained together; it would be impossible to make a change on one without destroying the chain.
Put simply, miners are security guards and accountants—they check, document and secure the system, and they are paid to do so.
Technically, this code is referred to as a hash.
What is a hash?
A hash is not a random number, it is a long sequence of random numbers and letters, but it is not a random number. It is the product of subjecting some data to a special formula. Take the word cat, as an example, and run it through the hash algorithm SHA-256 (the one used by Bitcoin), and it comes out as:
d7a8fbb307d7809469ca9abcb0082e4f8d5651e46d3cdb762d02d0bf37c9e592
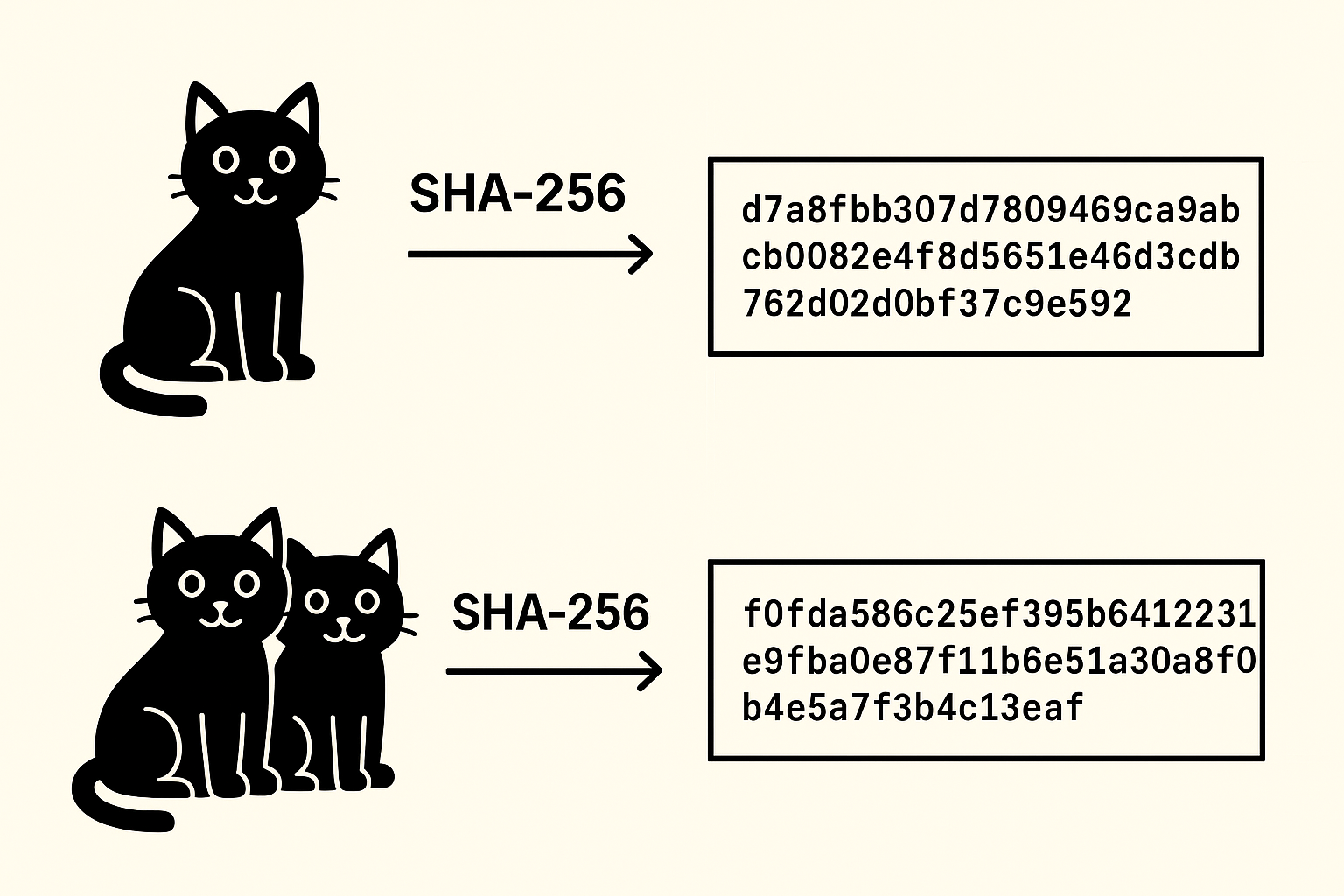
However, when you slightly adjust it to cats, the outcome is totally different:
f0fda586c25ef395b6412231e9fba0e87f11b6e51a30a8f0b4e5a7f3b4c13eaf
This tells us two things quite plainly:
- Any small modification in the input gives a completely different hash.
- The length of the input does not matter at all; the length of the hash remains constant.
In Bitcoin, the data to be hashed is the list of transactions in a block, rather than the words, and a few other details, such as the hash of the previous block. The output is a block hash of the whole block. When any single transaction within the block is altered, the hash is completely altered. This is why hashes are similar to seals; they ensure that the information within them has not been modified.
Why are Bitcoin miners required?
The reason why miners are required is that the system does not accept any hash. The hash of the new block must satisfy very strict conditions (e.g. it should start with some number of zeros). No way to shortcut the search for such a hash. The only method is trial and error: modify a small part of the data known as the nonce and rehash until the result satisfies the rule. That is why powerful computers are used by miners- to attempt billions of hashes per second.
- A hash is a special digital signature of information.
- It appears as an unchanging length of numbers and letters.
- It will prove that the data has not been modified.
Administration requires miners, since they do all the hard work of discovering special hashes that pass the system requirements, making the blockchain safe.
Mining in real life
Consider a classroom in which the educator poses a super-tough mathematics problem.
- It is solved by all students (miners).
- The first student who answers correctly will receive a chocolate (Bitcoin).
- All people can check the answer in the board (blockchain).
That’s how mining works.
What Are Bitcoin Wallets?
A wallet is your digital pocket, which is a Bitcoin wallet. It does not store Bitcoins themselves, but it stores the special keys that you need to access them on the blockchain. Consider it a device that allows you to send, get, and store your Bitcoin securely. You can not show that the Bitcoins on the blockchain are yours without a wallet.
A wallet has two very important parts inside:
- Public key- This is similar to your bank account number. You can share it with anybody so they can send you Bitcoin.
- Private key- This is similar to your ATM PIN. Only you should know it. In case somebody has to get it, they can steal your Bitcoin. And the loss of it costs you access to your Bitcoin permanently.
Wallets also come in various varieties based on how you intend to use and store your Bitcoin:
- Mobile or computer apps-These are basic apps that you install. They are convenient and simple to carry out everyday activities.
- Hardware wallets- Hardware wallets are tangible gadgets that store your keys in a safe offline location; thus, these are very vulnerable to hackers.
3. Paper wallets- You just have your keys ready on a piece of paper. So long as the paper is secure, your Bitcoin is secure as well.
Bitcoins do not reside in a wallet; the keys reside there. And the most crucial rule of owning Bitcoin is to keep your private key safe.
How Many Bitcoins Exist?
- Bitcoins will never be more than 21 million.
- Over 19 million have now been mined.
- This renders Bitcoin precious, just like gold.
- That is why they refer to Bitcoin as digital gold.
Why Does Mining Get Harder?
Back in the early days, anybody could mine Bitcoin with a regular computer and a CPU. New puzzles became more difficult as new miners came in, and people moved to much faster GPUs. However, after a short time, even gaming computers were not enough.
Mining is now a job of special machines known as ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits). Where a normal computer can only make millions of hashes per second, ASICs can make trillions.
This has made them thousands of times stronger, yet very power-hungry, and they can easily consume more electricity than a few appliances in the house. This is the reason why mining is no longer done at home but at massive mining farms with hundreds of ASICs running in paralleled to one another.
Would you like me to further simplify this and resort to a basic comparison with real-life (e.g. one ASIC = thousands of laptops)
Halving- Reason: Rewards are continuing to decline
Bitcoin already has a policy in place to ensure that it does not over-issue coins to the world. This rule is called halving. The amount of reward miners receive with each block added to the blockchain is reduced by half every 4 years. This makes Bitcoin rare, as gold is also made difficult to retrieve as time progresses.
The reward was 50 BTC per block when Bitcoin was launched in 2009. It fell to 25 BTC in 2012, and then 6.25 BTC in 2020, and in 2025, it will be only 3.125 BTC per block. This cycle will repeat until every 21 million Bitcoins have been mined.
At some point, block rewards will be zero. That is when miners will not receive new Bitcoins as rewards. They will instead make money on the transaction fees people will pay when sending Bitcoin.
In short:
- Halving happens every 4 years.
- It halves the miner’s rewards every time.
- It makes the supply of Bitcoin scarce and restricted.
- Miners will be able to depend on transaction fees only in the future.
Advantages of Bitcoin
- No middleman: Send money directly.
- Fast: Works 24/7, unlike banks.
- Global: Send money anywhere.
- Secure: Impossible to fake or double-spend.
- Limited supply: It can’t be printed like normal money.
Problems with Bitcoin
- Energy use: Mining takes a lot of electricity.
- Volatile: Prices can rise and fall quickly.
- Not widely accepted: You can’t spend it everywhere yet.
Bitcoin mining is the heartbeat of the Bitcoin network. It keeps the system safe, fair, and decentralised.
To remember easily:
- Blockchain = Giant notebook.
- Miners = Students solving puzzles for rewards.
- Wallet = Digital pocket with secret keys.
- Bitcoin = Digital gold, limited and valuable.
Even though it sounds technical, at its heart, Bitcoin is about people trusting a system without needing banks.
FAQs ( Frequently Asked Questions )
Initially, yes, anybody could mine Bitcoin using a regular computer. However, today, mining involves the use of extremely powerful and expensive machines known as ASICs, and they consume a lot of electricity. A normal human with a home computer or even a high-performance gaming PC has no chance to compete with large mining farms.
A new block of Bitcoin is mined on average every 10 minutes around the globe. However, due to millions of strong computers trying to outcompete each other, it is hardly possible to mine a block on your own. This is the reason why individuals tend to join the mining pools where numerous miners pool their power and distribute the rewards.
Mining Bitcoin is not prohibited by law in most countries, provided you pay the electricity bills and comply with the local legislation. But mining has been outlawed or limited in some nations as it consumes a lot of energy.
Yes, it is legal to mine Bitcoin in India. There is no law that bans it. However, there are still no specific government regulations, so miners should be cautious regarding aspects such as the cost of electricity, taxes, and the manner in which they spend their mined Bitcoin.
Mining is or can be lucrative, and it relies on:
- The price of power where you live.
- The Bitcoin value then.
- The strength and the efficiency of your mining machine.
Big mining farms may be profitable in countries where electricity is cheap. In the majority of cases, though, equipment and electricity are a little more expensive than the payoff, so at home it is not always profitable.
I left my engineering job to follow my true passion writing and research. A passionate explorer of words and knowledge, I find joy in diving deep into topics and turning rich, insightful research into compelling, impactful content. Whether it’s storytelling, technical writing, or brand narratives, I believe that the right words can make a real difference.

